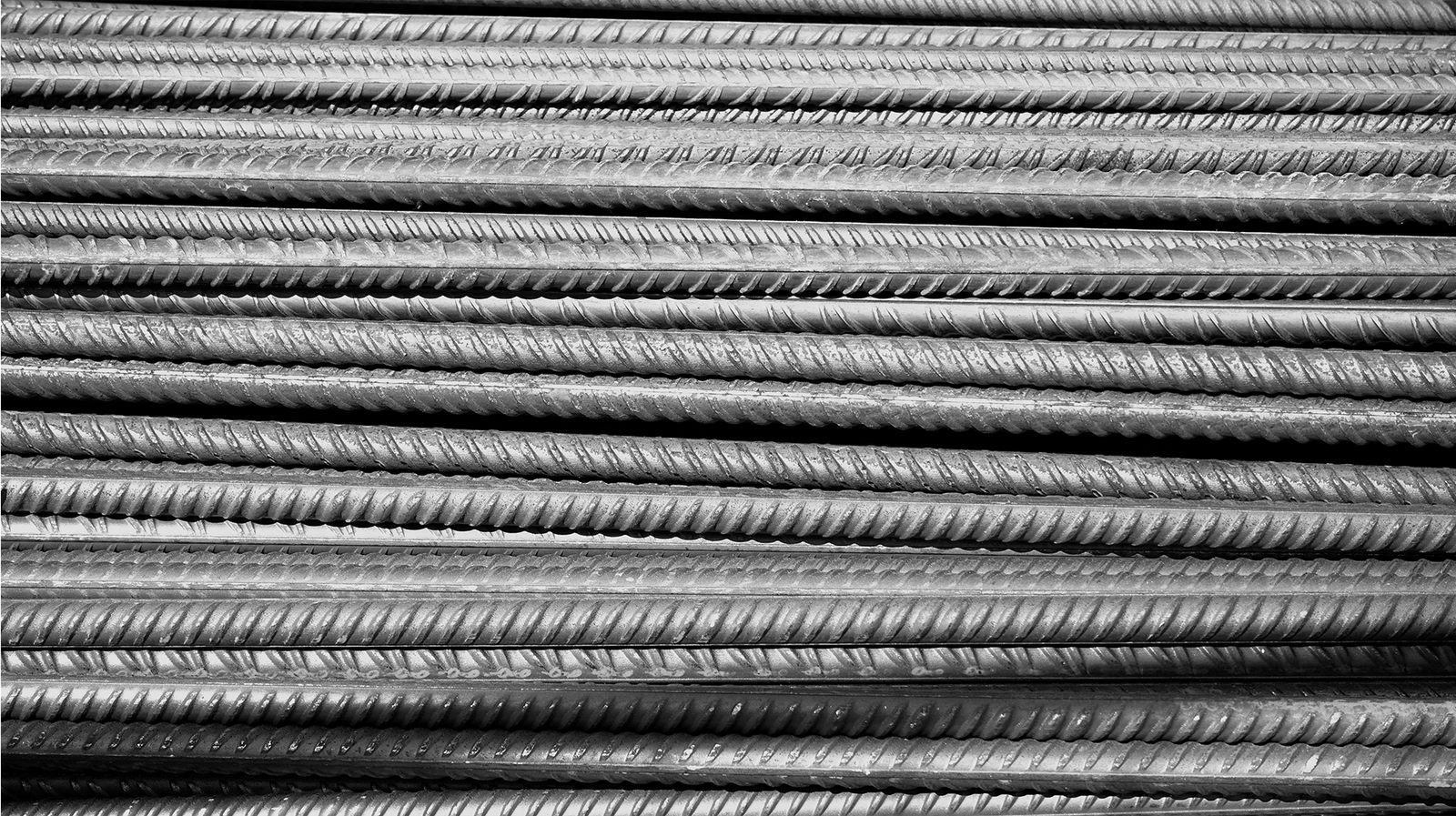
STEEL
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, with carbon content typically ranging from 0.02% to 2.0%, and may also contain other alloying elements such as manganese, chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium to enhance specific properties. It is one of the most widely used engineering and construction materials in the world, valued for its high strength, durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Steel offers an excellent balance of mechanical strength, formability, weldability, and recyclability, making it a backbone material for modern infrastructure and industrial development.
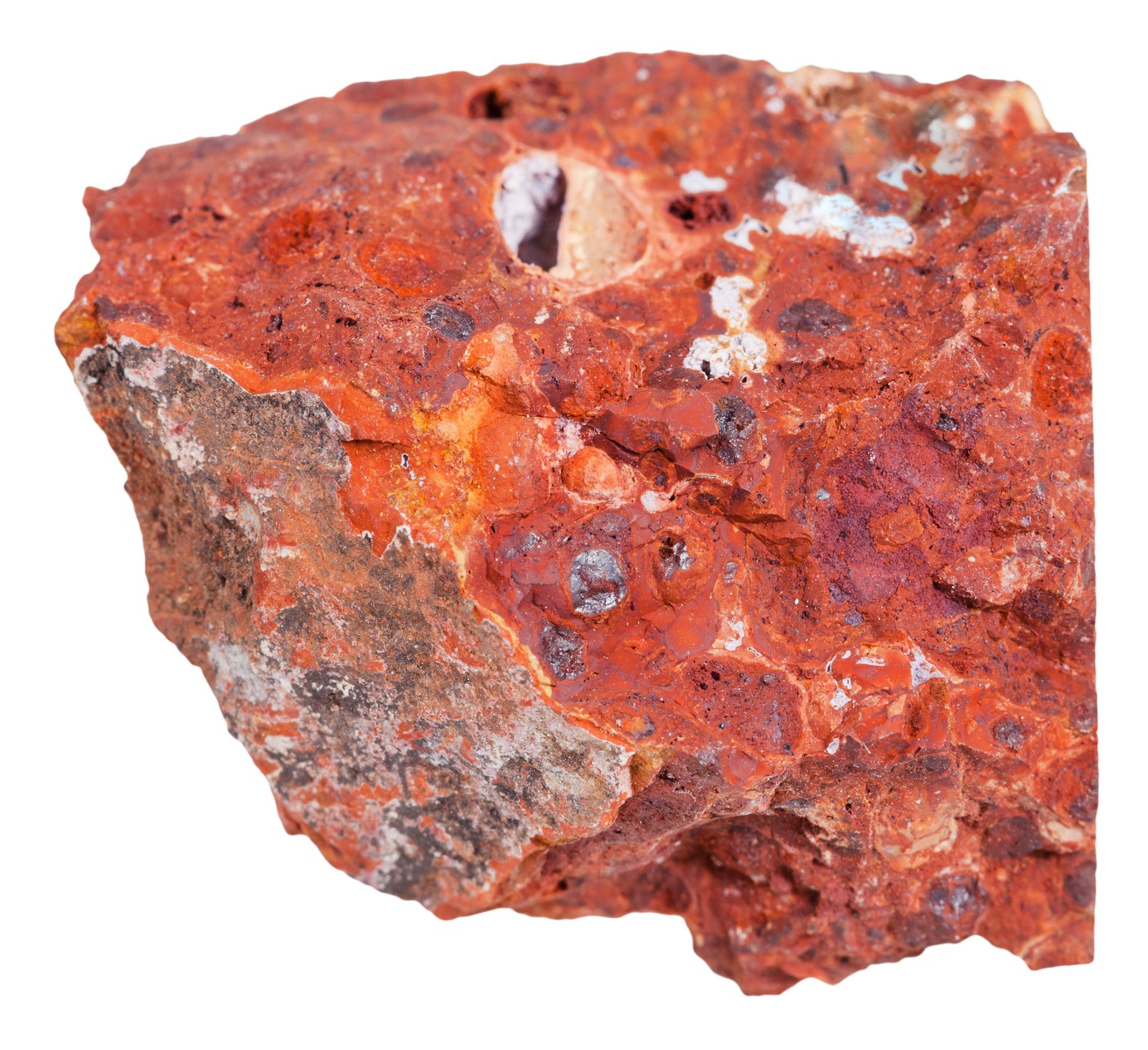

Bauxite
Bauxite is a lightweight, silver-white metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high malleability, and impressive strength-to-weight ratio. It is the most widely used non-ferrous metal globally and plays a critical role in industries ranging from construction and transportation to electrical and packaging. Its natural oxide layer protects it from rusting, making aluminium a preferred material for long-term, durable applications.

Aluminium
Aluminium is a lightweight, silver-white metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high malleability, and impressive strength-to-weight ratio. It is the most widely used non-ferrous metal globally and plays a critical role in industries ranging from construction and transportation to electrical and packaging. Its natural oxide layer protects it from rusting, making aluminium a preferred material for long-term, durable applications.
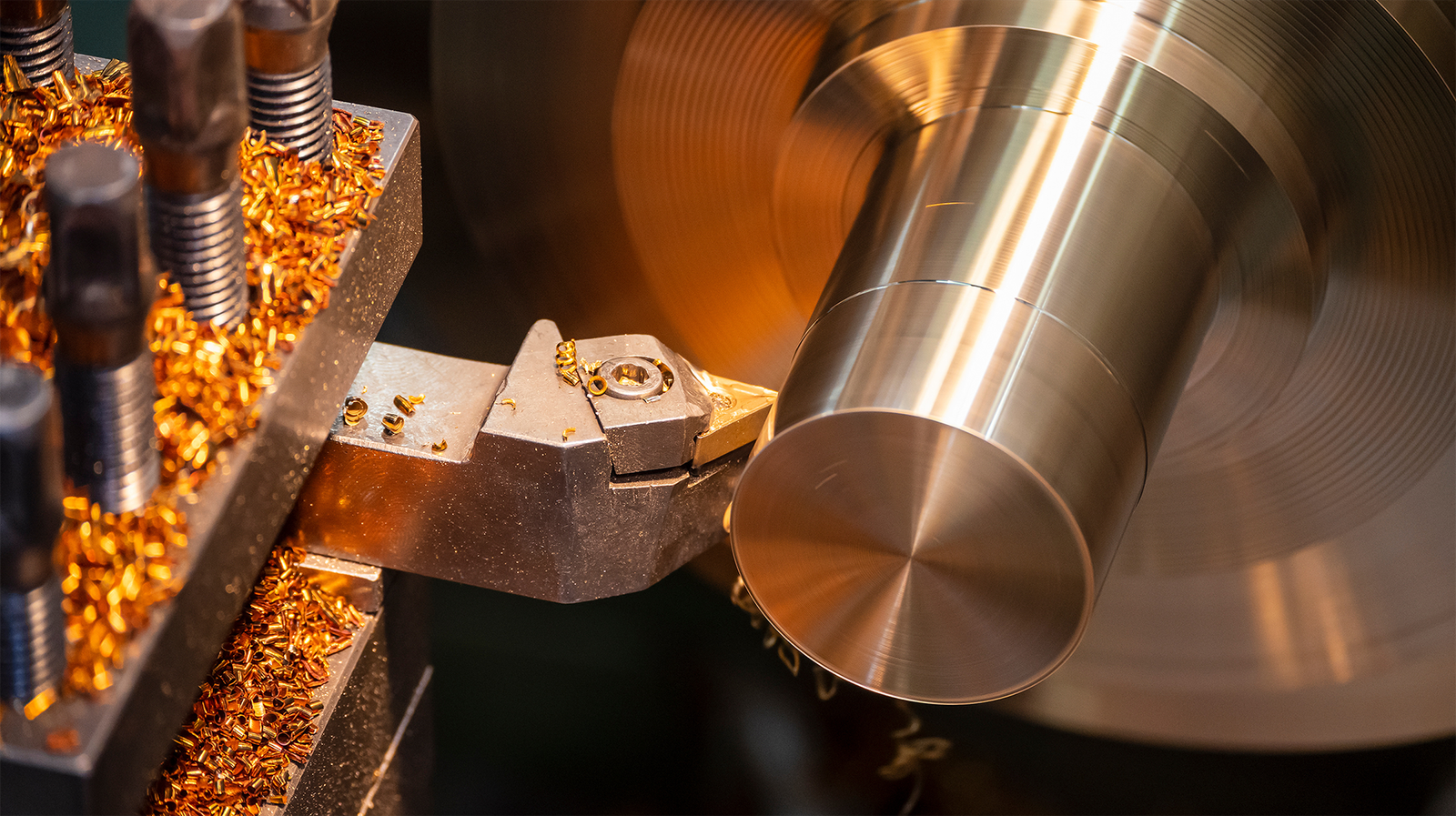

Bronze
Bronze is a copper-based alloy primarily composed of copper and tin, with small amounts of elements such as aluminium, phosphorus, silicon, and manganese to enhance strength and corrosion resistance. Known as one of the earliest engineered alloys, bronze is widely valued for its excellent durability, low friction, and resistance to wear and corrosion—making it ideal for mechanical components and decorative applications. Its rich golden-brown appearance and long service life make bronze a preferred metal across industries including marine, electrical, machinery, and art.

Zinc
Zinc is a bluish-white, lustrous metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, ability to form protective coatings, and versatility in alloy production. It is the fourth most widely used metal after iron, aluminium, and copper. One of its most important roles is galvanizing, where zinc acts as a sacrificial coating to protect steel from rusting. Zinc is also vital in die-casting, battery manufacturing, and producing alloys such as brass. Zinc is fully recyclable, energy-efficient to process, and widely used across construction, automotive, electrical, and chemical industries.

Iron
Iron is one of the most widely used metals due to its strength, durability, and abundance. It forms the foundation of steel and numerous alloys used across construction, automotive, machinery, and manufacturing industries worldwide.
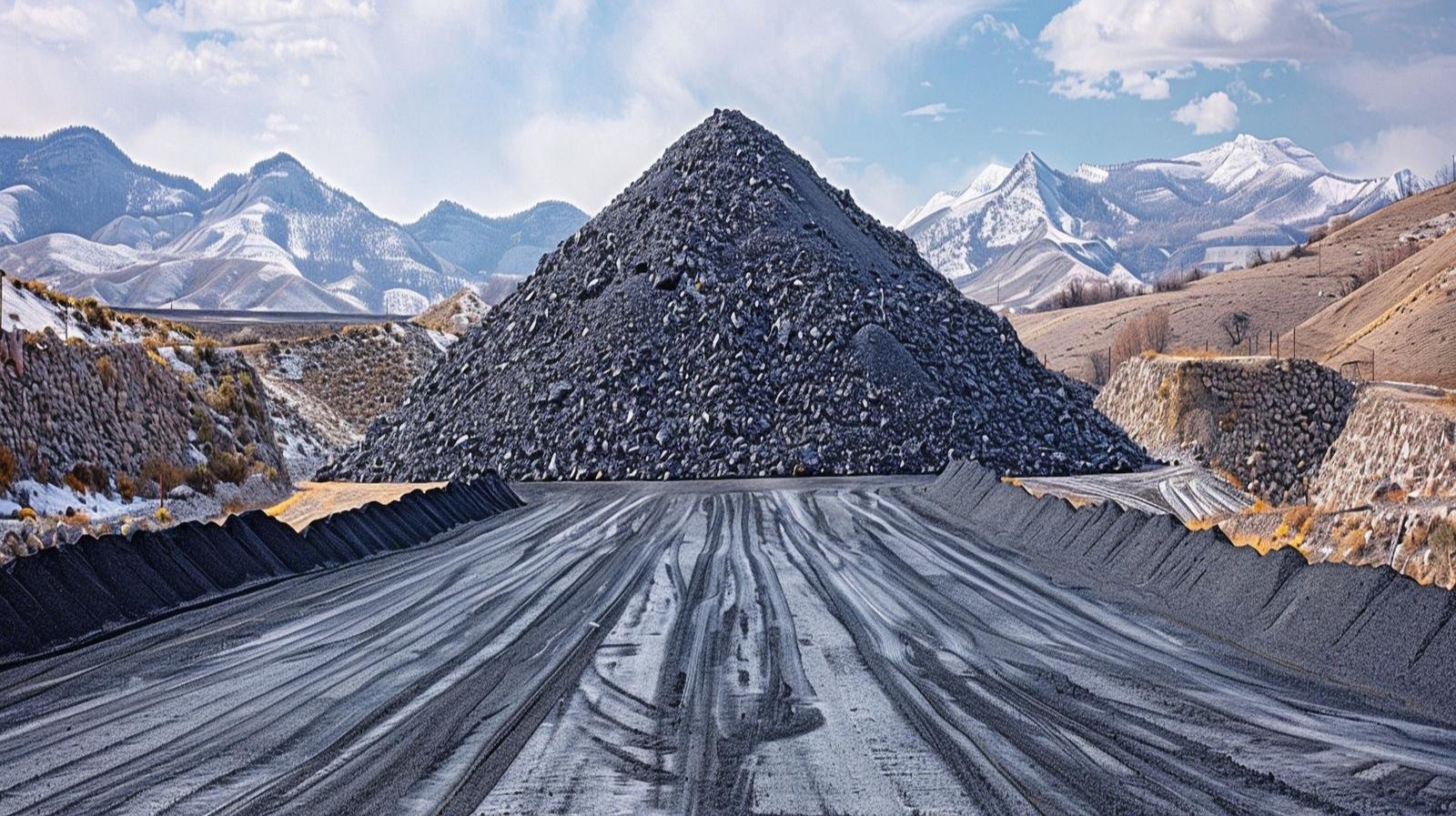

Iron Ore
Iron ore is a naturally occurring mineral from which iron metal is extracted and is one of the most important raw materials used in the production of steel. It mainly consists of iron oxides and varies in color from dark grey and brown to reddish shades depending on its composition. Iron ore is commonly found in the Earth’s crust and is mined through open-pit or underground methods. The most important types of iron ore include hematite, magnetite, limonite, and siderite, each differing in iron content and properties. Iron obtained from iron ore is widely used in construction, machinery, transportation, and manufacturing industries, making iron ore a vital resource for industrial development and economic growth.

Brass
Brass is a versatile copper–zinc alloy known for its bright golden appearance, excellent workability, and superior corrosion resistance. The zinc content (typically 5% to 40%) determines its strength, color, and forming characteristics. Because of its combination of strength, durability, and aesthetics, brass is widely used in electrical, plumbing, decorative, and industrial applications. Its excellent machinability and resistance to tarnish make it one of the most important engineering alloys.

Copper
Copper is a reddish-brown, highly conductive metal known for its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability. It is one of the oldest metals used by humans and remains a critical industrial material today. Its ability to conduct electricity efficiently, resist corrosion, and form into various shapes makes it indispensable across electrical, construction, manufacturing, and transportation industries. Copper is also fully recyclable without losing its properties, making it a sustainable material for modern applications..

Titanium
Titanium is a strong, lightweight, and highly corrosion-resistant metal known for its exceptional performance in demanding environments. It has a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent biocompatibility, and outstanding resistance to corrosion from seawater, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Titanium is widely used in aerospace, medical implants, marine engineering, chemical processing, automotive, and high-performance industrial applications. Its combination of low density, high strength, and long service life makes it one of the most valuable metals for advanced technologies and critical components.

Tin
Tin is a soft, silvery-white metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, low melting point, and exceptional ability to bond with other metals. It is widely used as a protective coating for steel and copper to prevent rusting and is an essential ingredient in many important alloys such as bronze, solder, and pewter. Tin does not oxidize easily and maintains its luster over long periods, making it suitable for food-safe applications, electrical components, and decorative uses. It is highly valued in the electronics industry due to its excellent solderability.

Lead
Lead is a dense, soft, malleable, and corrosion-resistant metal widely used across industrial sectors due to its unique physical properties. It is a bluish-grey metal known for its high density, low melting point, excellent sound insulation, and superior resistance to chemicals and moisture. Lead is also one of the best materials for radiation shielding, making it essential in the medical, nuclear, and electronics industries. Its ease of fabrication, recyclability, and durability make it a valuable material in several engineering applications.

Magnesium
Magnesium is a lightweight, silvery-white metal known as one of the lightest structural materials in the world. It is approximately 75% lighter than steel and 33% lighter than aluminium, making it highly valuable in industries requiring strength with minimal weight. Magnesium is also highly machinable, recyclable, and offers excellent vibration damping, making it essential for automotive, aerospace, electronics, and industrial manufacturing. Magnesium is primarily used in alloy form because pure magnesium is soft; alloying with aluminium, zinc, manganese, and rare-earth elements significantly increases its strength and durability.

Nickel
Nickel is a strong, lustrous, silvery-white metal widely valued for its corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent alloying ability. It is one of the most versatile industrial metals, used extensively to produce stainless steel, superalloys, plating materials, and battery components. Nickel’s ability to withstand extreme environments—heat, pressure, and aggressive chemicals—makes it critical for industries such as energy, aerospace, chemical processing, marine, and electronics.
Cobalt
Cobalt is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray transition metal known for its high strength, excellent wear resistance, and outstanding performance at elevated temperatures. It is a critical industrial metal widely used in superalloys, batteries, cutting tools, magnets, pigments, and chemical catalysts. Cobalt retains its mechanical strength at high temperatures and exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it indispensable in demanding industrial and high-performance applications.

Tungsten
Tungsten, also known as Wolfram (chemical symbol: W), is a rare, extremely strong and dense metal best known for having the highest melting point of all metals. It is valued for its exceptional hardness, heat resistance, wear resistance, and strength at elevated temperatures. Because of these unique characteristics, tungsten is widely used in aerospace, defense, tooling, electronics, mining, and high-temperature industrial applications where other metals fail.

Gold
Gold is a precious, noble metal known for its distinctive yellow color, exceptional corrosion resistance, and outstanding electrical conductivity. Chemically symbolized as Au, gold does not oxidize or tarnish, making it one of the most stable and valuable metals known to humanity. Due to its high malleability, ductility, and reliability, gold is widely used in jewelry, electronics, investment, medical, aerospace, and industrial applications. It has been used as a store of value and a medium of exchange for thousands of years and continues to be a critical material in modern technology.

Silver
Silver is a precious, lustrous white metal known for having the highest electrical and thermal conductivity of all metals. It is highly valued for its excellent corrosion resistance, superior reflectivity, and outstanding workability. Silver has been used for thousands of years in coinage, jewelry, electronics, medical applications, and industrial manufacturing, making it one of the most versatile precious metals in the world.
Platinum
Platinum is a precious, dense, silvery-white metal belonging to the platinum group metals (PGMs). It is highly valued for its exceptional corrosion resistance, thermal stability, catalytic activity, and electrical reliability. Platinum does not oxidize or tarnish in air, even at high temperatures, making it one of the most durable and chemically stable metals available. Because of its unique physical and chemical properties, platinum is widely used in automotive, chemical processing, electronics, medical, jewelry, and energy industries.
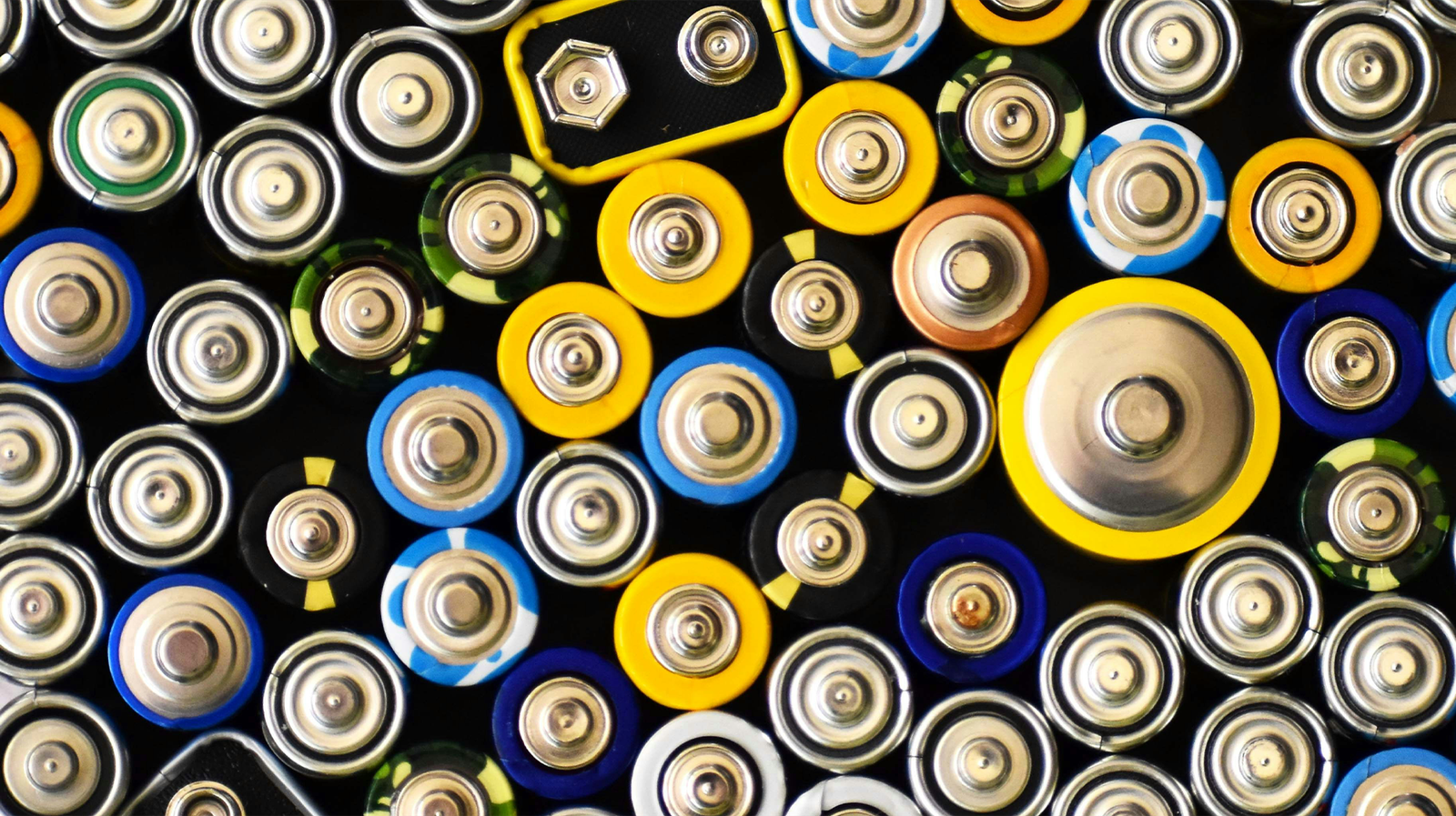

Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal and the lightest solid element on the periodic table. It is highly reactive and does not occur freely in nature; instead, it is found in minerals (such as spodumene, lepidolite) and brine deposits. Due to its exceptional electrochemical properties and low density, lithium has become a strategic material for modern industries, especially energy storage, electronics, aerospace, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals.
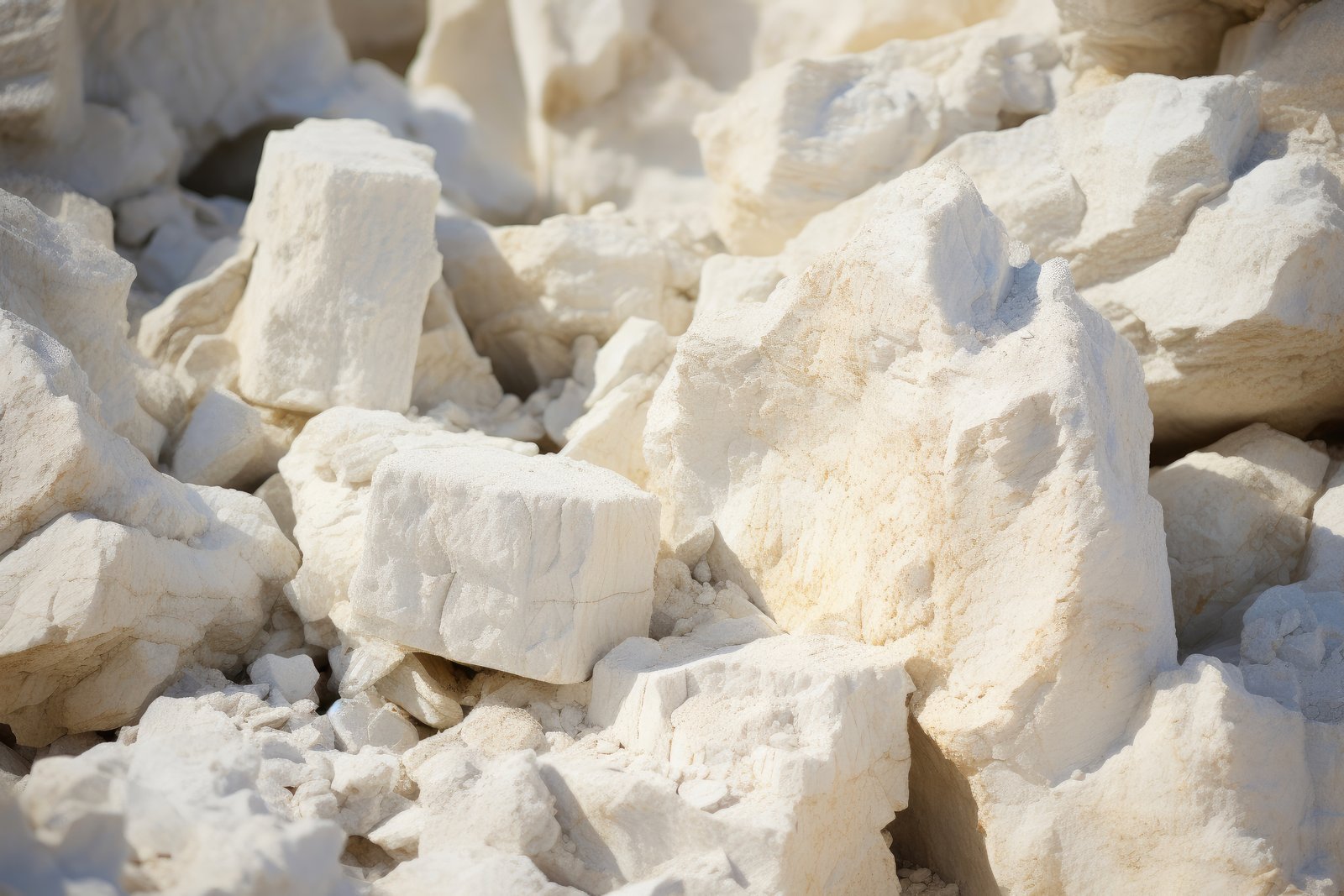

Limestone
Lithium is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal and the lightest solid element on the periodic table. It is highly reactive and does not occur freely in nature; instead, it is found in minerals (such as spodumene, lepidolite) and brine deposits. Due to its exceptional electrochemical properties and low density, lithium has become a strategic material for modern industries, especially energy storage, electronics, aerospace, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals.

Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO₄·2H₂O). It is widely used in construction, agriculture, and industrial applications due to its excellent physical properties, abundance, and ease of processing. Gypsum occurs naturally in sedimentary rock formations, often associated with minerals like anhydrite, calcite, and halite. It is colorless to white in its pure form but can appear in shades of gray, yellow, red, or brown due to impurities.

Rare Earth Elements (REEs)
Rare Earth Elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar metallic elements that play a critical role in modern technology and clean energy applications. They include the 15 lanthanides (from Lanthanum to Lutetium), along with Scandium and Yttrium. Despite their name, REEs are not truly rare, but they are rarely found in concentrated, economically extractable forms, which makes their mining and processing complex. REEs possess unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties, making them essential for high-performance magnets, electronics, renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, aerospace, defense, and medical equipment.

